Feb. 16, 2022[INSIDE REGENERATIVE MEDICINE]
What is cell culture to begin with?
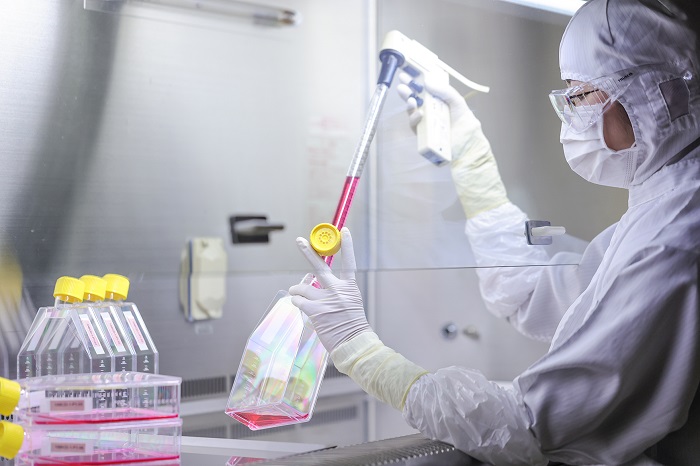

Thus far we have discussed various aspects of regenerative medicine. In such discussions, the term “cell culture” naturally comes up. Hearing this, I think you probably can imagine that it means taking cells from inside our bodies to increase them outside of the body. But people who have actually tried cell culture are few and far between. For this reason, I’d like to take a little closer look at cell culture in this installment.
In the past, cell culture using the cells of animals, including humans, was a tool for advancing biological research. Human and animal cells were propagated outside the body so that researchers could observe the detailed workings of the cells themselves along with the beneficial results of various drugs and adverse reactions to them. A culture solution rich in nutrients is used in cell culture. The performance of culture solution is enhanced by adding body constituents such as human or animal blood. The solution is supplemented with the ingredients that cells need in order to grow. Warming the cells in the culture solution to the same temperature as the human body (37ºC) causes them to divide and grow.
Broadly speaking, there are two types of cell culture. One is the type where the cells adhere to something in order to grow, and the other is the type where the cells themselves proliferate while suspended in the culture solution. Most of the cells in the body that make up the skin, bones, cartilage, and various organs grow while adhering to something. In contrast, blood cells survive in a suspended state and proliferate as well. In the world of cell culture, we do our best to recreate the state in which cells exist in the body.
It used to be no easy thing to culture the cells in our bodies directly. In some cases, the cells could not survive in the special environment of cell culture; in others, they survived but were unable to maintain the functions they normally had in the body. That is why researchers in the past used cancer cells, etc., to artificially create cells that could be grown as stably as possible for use as tools in research. Cells of this kind had aspects that expressed the functions of our body, but they also had completely different aspects. Nevertheless, the fact that they could be produced in large quantities made them suitable for conducting the same kind of research throughout the world.
With further advances in cell culture technology, it has become possible to culture human cells as is. The cultured skin that we handle in our business is a representative example of this. We are now able to grow large quantities of cells that retain the functions of skin. However, other cells, such as liver cells, will grow vigorously within the body but scarcely increase at all in the culture environment. It appears that cells with complex functions cannot easily be increased.
Innovative cell culture technology has made it possible to increase and revitalize the cells in patients’ bodies. The essence of regenerative medicine lies in serving as a point of contact between biotechnology and medicine. In the future, we expect to be able to provide more kinds of cells that proffer more kinds of value.
February 16, 2022