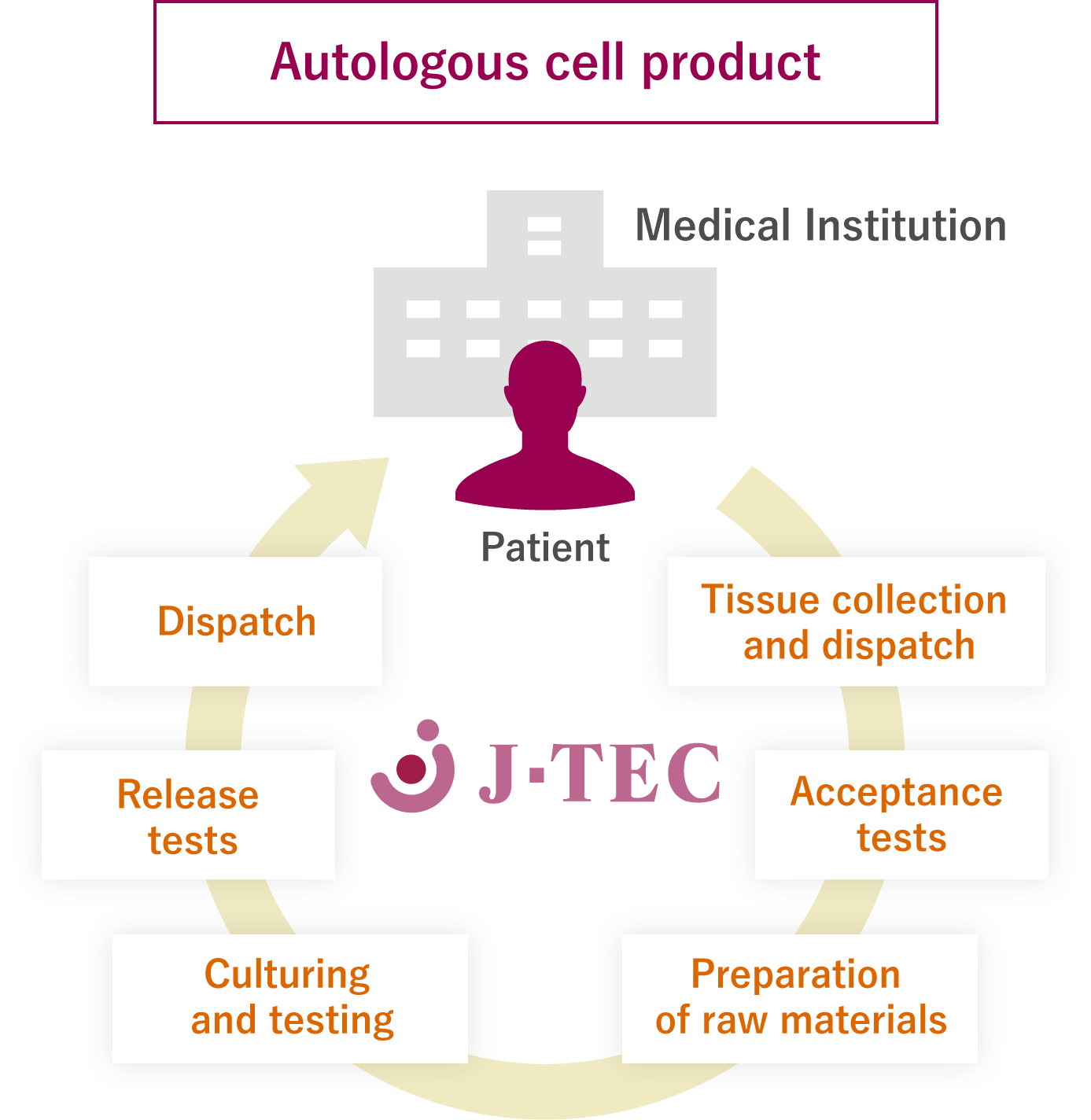
Regenerative medicine using patients' own cells (autologous cells)
and other people's cells (allogeneic cells)
Regenerative medicine using patients' own cells
(autologous cells)
Treatment using patients' own cells. This is fundamentally different from manufacturing conventional pharmaceutical products and medical devices.
The autologous cultured epidermis, autologous cultured cartilage, autologous cultured corneal epithelium, and the autologous CAR-T-cell treatment marketed or being developed by J-TEC are regenerative medical products that use the patients' own cells (autologous cells).
Characteristics
- Since the cells belong to the patients, the risk of rejection is very low, and the products are very safe.
- The products are order made for each case that arises and treatment takes some time.
Flow
- A physician collects normal tissue from an uninjured site on the patient in question.
- J-TEC cultures tissue-processed cells, performs release tests and packaging, and dispatches the product to the medical institution.
- A physician performs transplantation surgery on the patient in question.
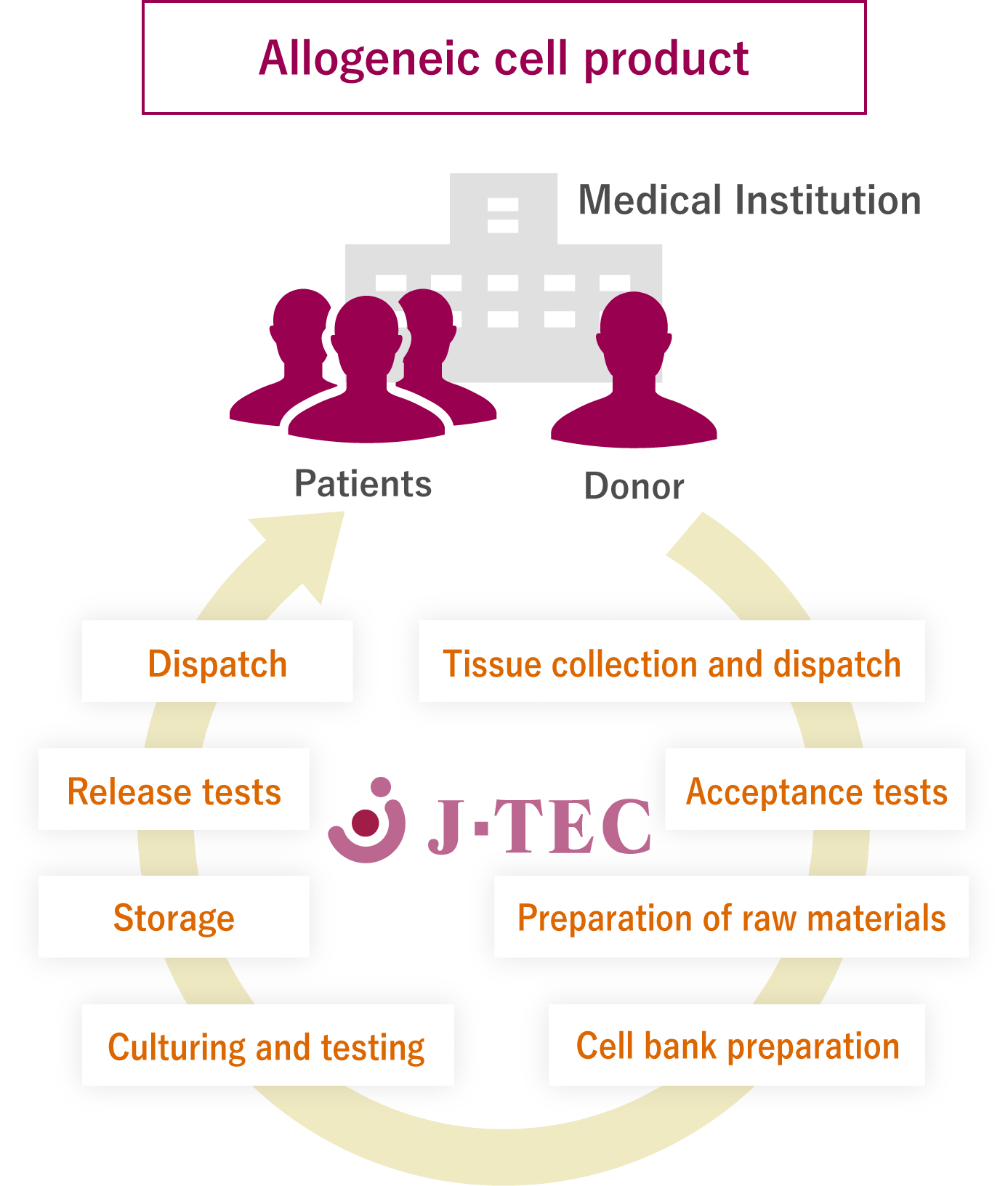
Regenerative medicine using other people's cells
(allogeneic cells)
As well as building a model for the supply of regenerative medical products using autologous cells, J-TEC has also been involved in the development of products that use allogeneic cells.
J-TEC's allogeneic cultured epidermis is a product that uses other people's cells (allogeneic cells).
Characteristics
- Allogeneic cells can be prepared in advance and used immediately when required.
- Since the cells do not belong to the patient, the graft will ultimately be rejected, but it can be used as a stop-gap treatment until treatment with autologous cells is available.
Flow
- A physician collects normal tissue from an uninjured site on a donor.
- J-TEC prepares a cell bank from tissue-processed cells, cultures, performs storage, release tests, and packaging, and dispatches the product to the medical institution.
- A physician performs transplantation surgery on the patient.